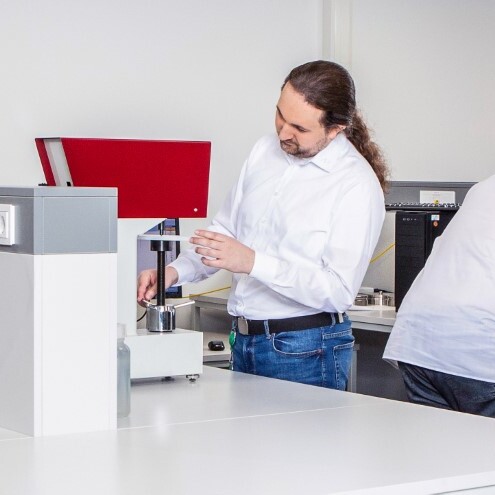

We put our materials to the test:
Our materials are performance tested for a wide variety of scenarios. In order to meet specific customer requirements, we carry out both standard tests according to ISO standards as well as custom tests. Our goal is to accurately and reliably determine the performance properties of our materials–from surface resistance to melt index and bendability–at all times so as to ensure that our materials meet our expectations for durability and quality.
Density determination:
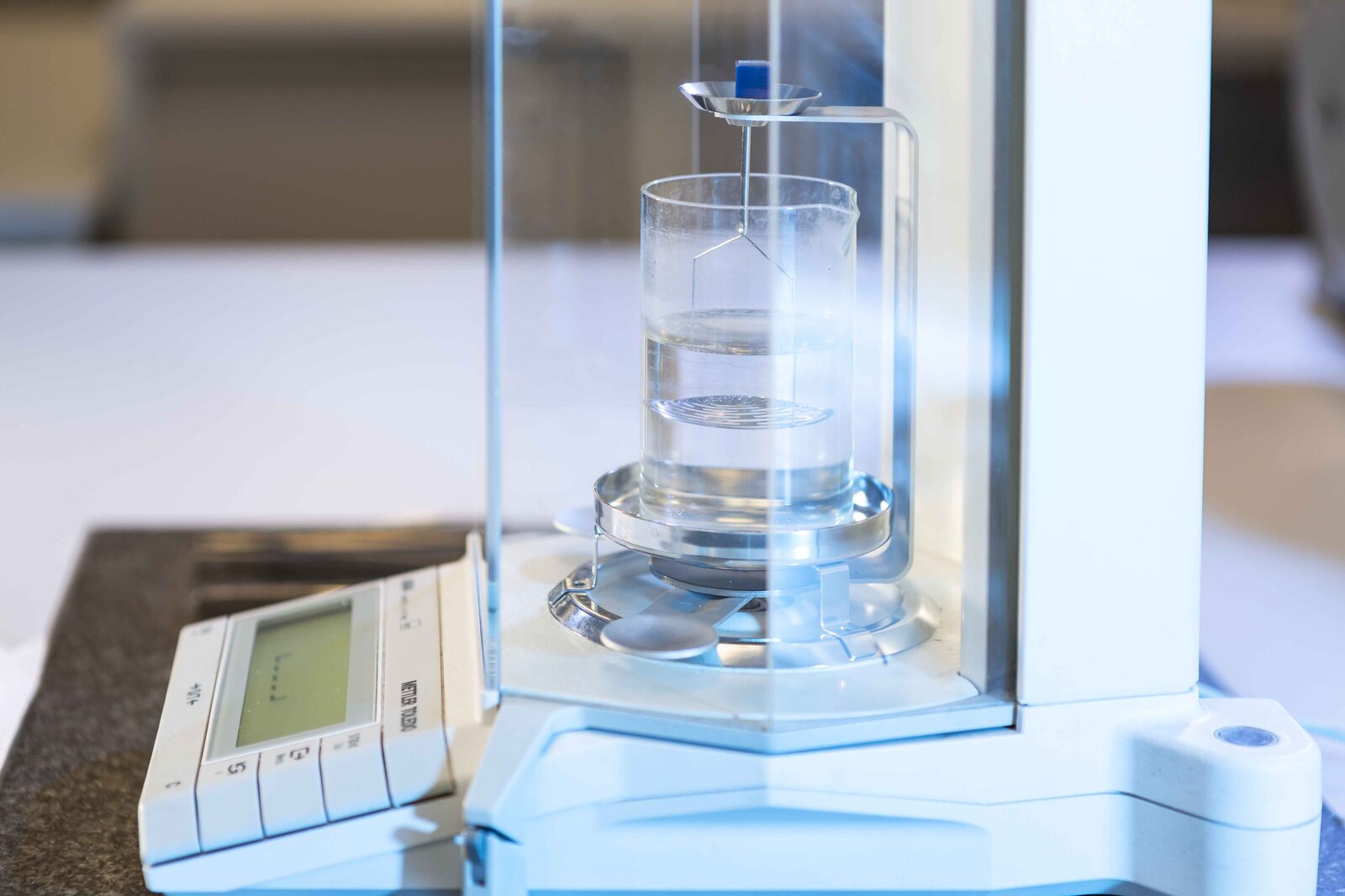

Density determination is a method of measuring the density of a material, which indicates how much mass is present in a given volume. The material is immersed in a liquid and the displaced volume of liquid is equal to the volume of the material. The mass of the displaced volume of liquid is then used to determine the density.
Notched Impact Test:
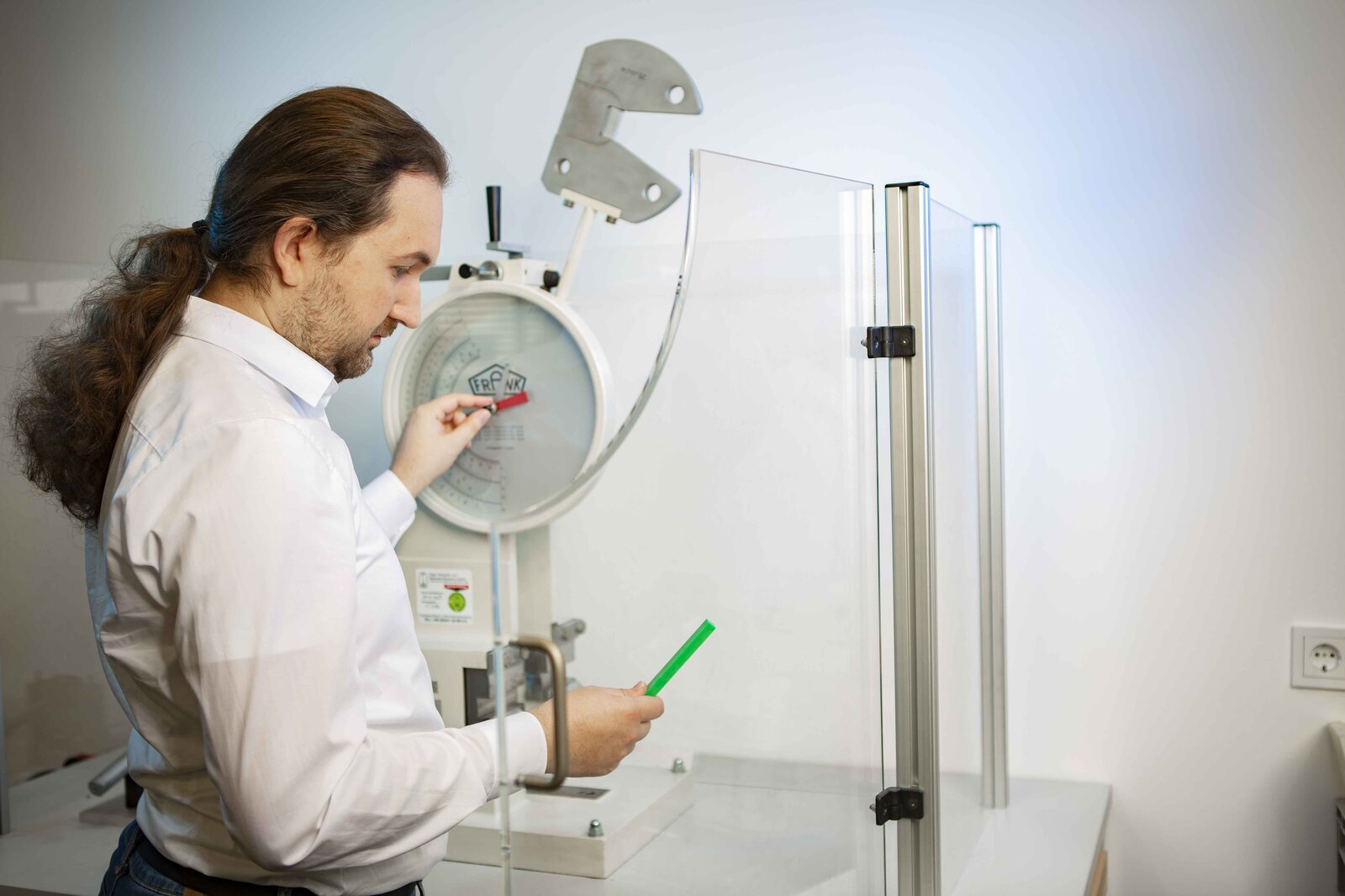

The impact test is a mechanical test used to determine the toughness of a material, specifically its ability to absorb energy during rapid fracture. An elongated, double-notched specimen is subjected to an impact load in a standard laboratory environment.
Friction Coefficient Measurement:
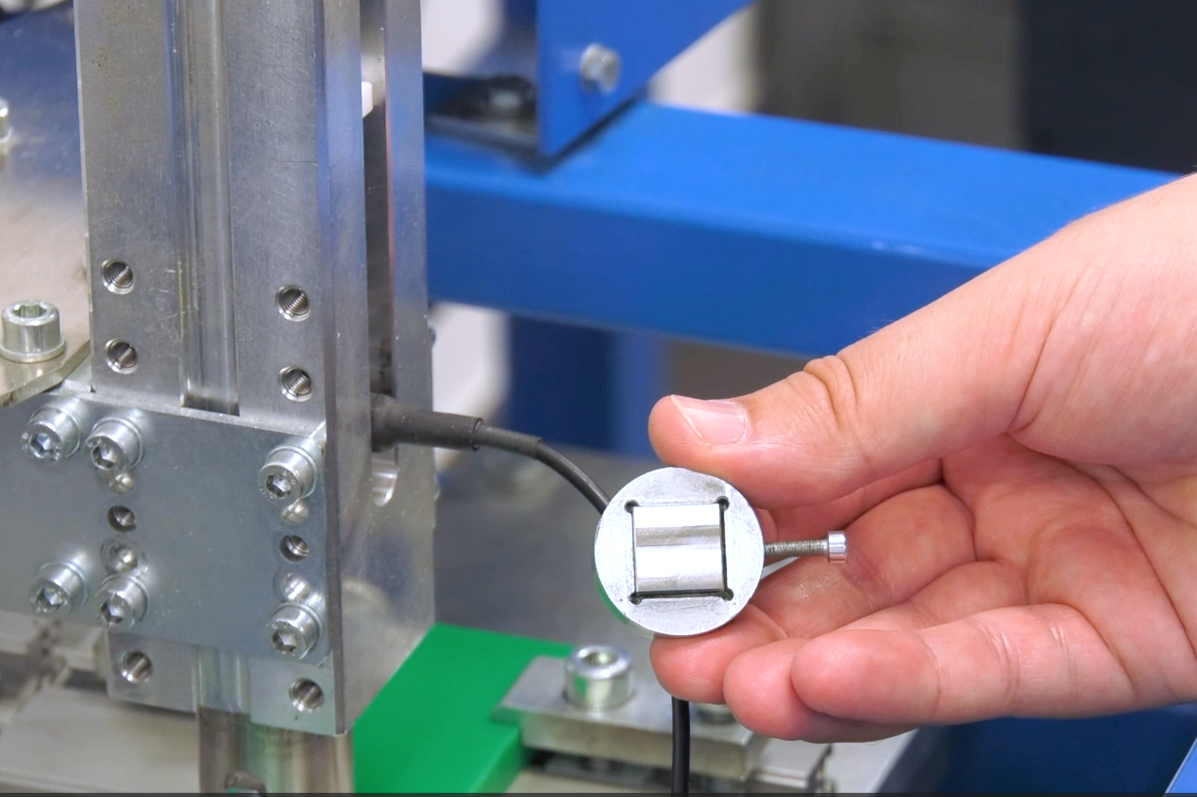
The coefficient of friction of a material is determined by measuring the coefficient of friction. It describes the relationship between two forces - the frictional force and the contact force. These occur when two bodies stick, slide, or roll against each other. The test body is pressed against a base body with a defined normal force. The resulting frictional forces try to counteract this movement. This is followed by the long-term wear test, which helps to investigate how the coefficient of friction changes or adapts over a longer period of time.
Ball Pressure hardness:
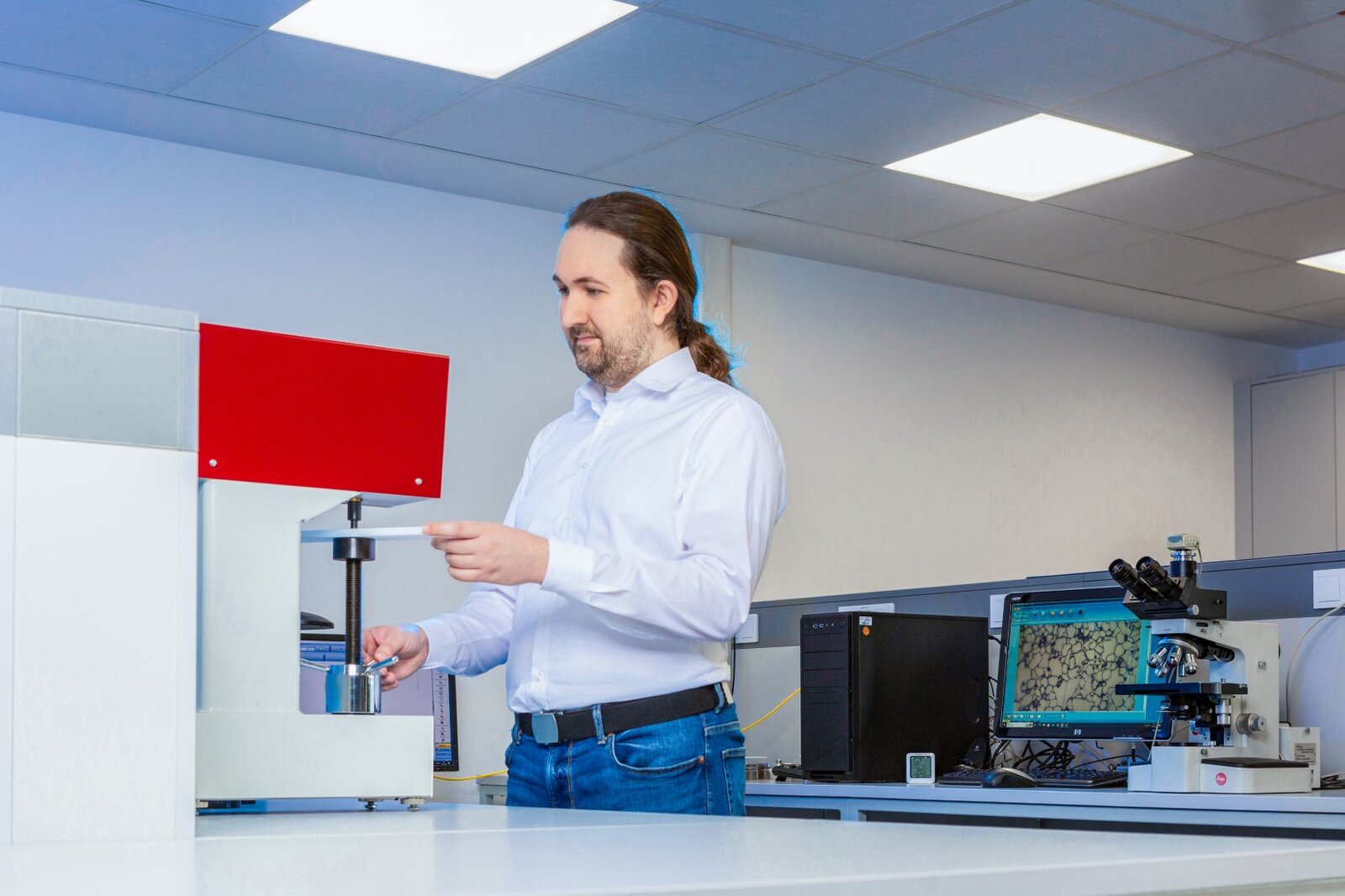

The ball indentation method was introduced to determine the hardness of plastics. This method measures the penetration depth of a steel ball into the surface of a test specimen under the impact of a test force. This test force acts for a defined period of time after a preload has been applied. The fundamental difficulty of this method is that the depth of penetration is not a linear function of the load. This is compensated for by limiting the penetration depth to a value that is small compared to the diameter of the ball.
Shore Durometer:
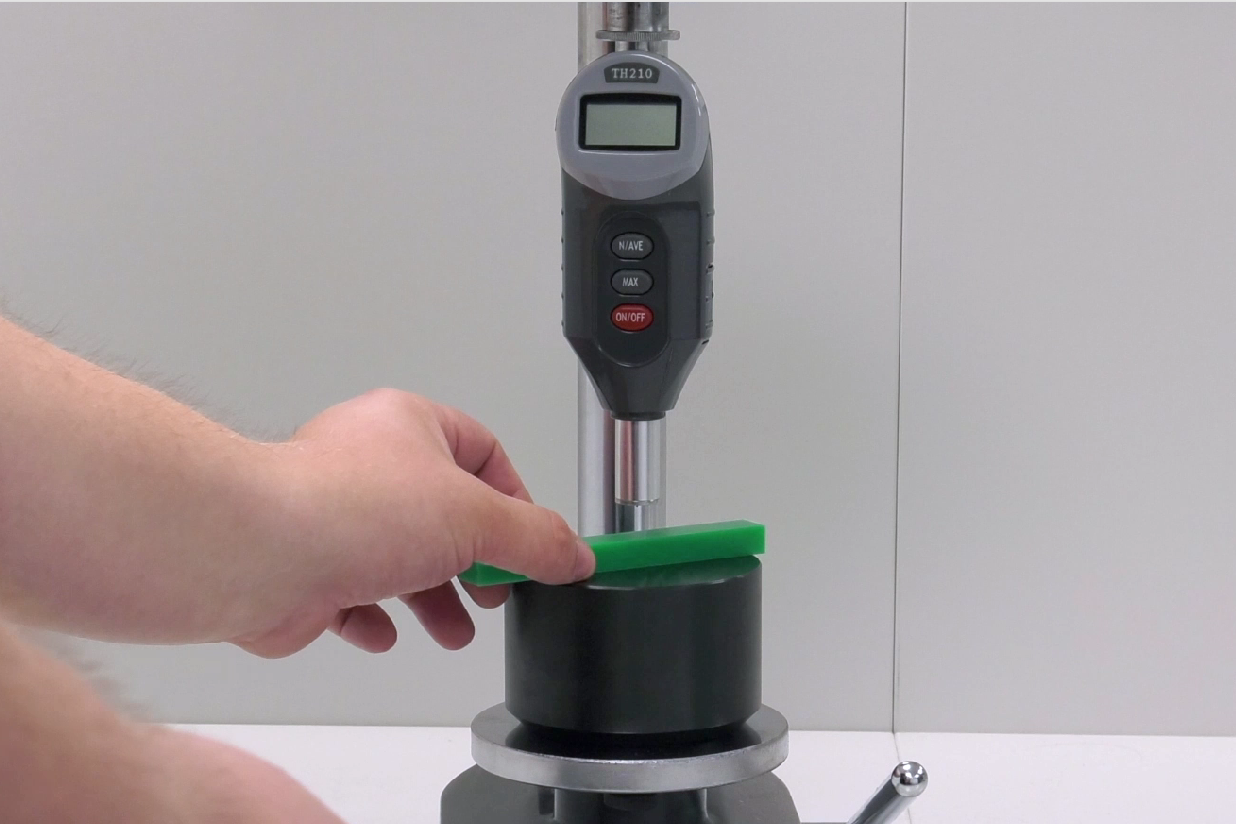

Like many other hardness tests, the DIN EN ISO 868 Shore Durometer measures the depth of a depression in the material that is created by a given force on a standardized indenter
Sand-Slurry-Test:
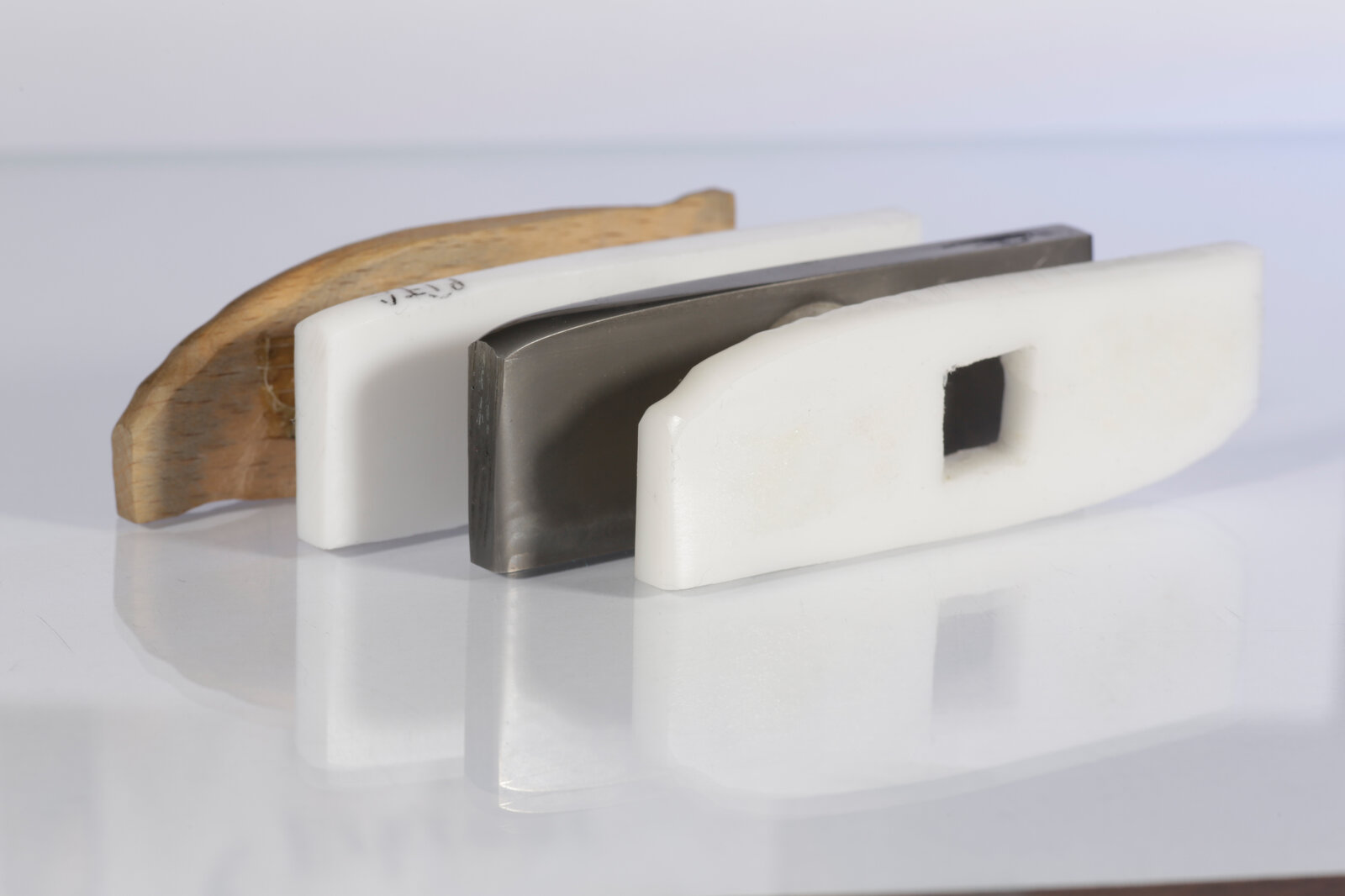

The sand slurry test is used to test the abrasion resistance of materials.The materials are exposed to an abrasive sand-water mixture on heavy rotation for 24 hours. This makes it possible to simulate a long service life as well as the wear behavior of the plastics.
Electrical resistance:
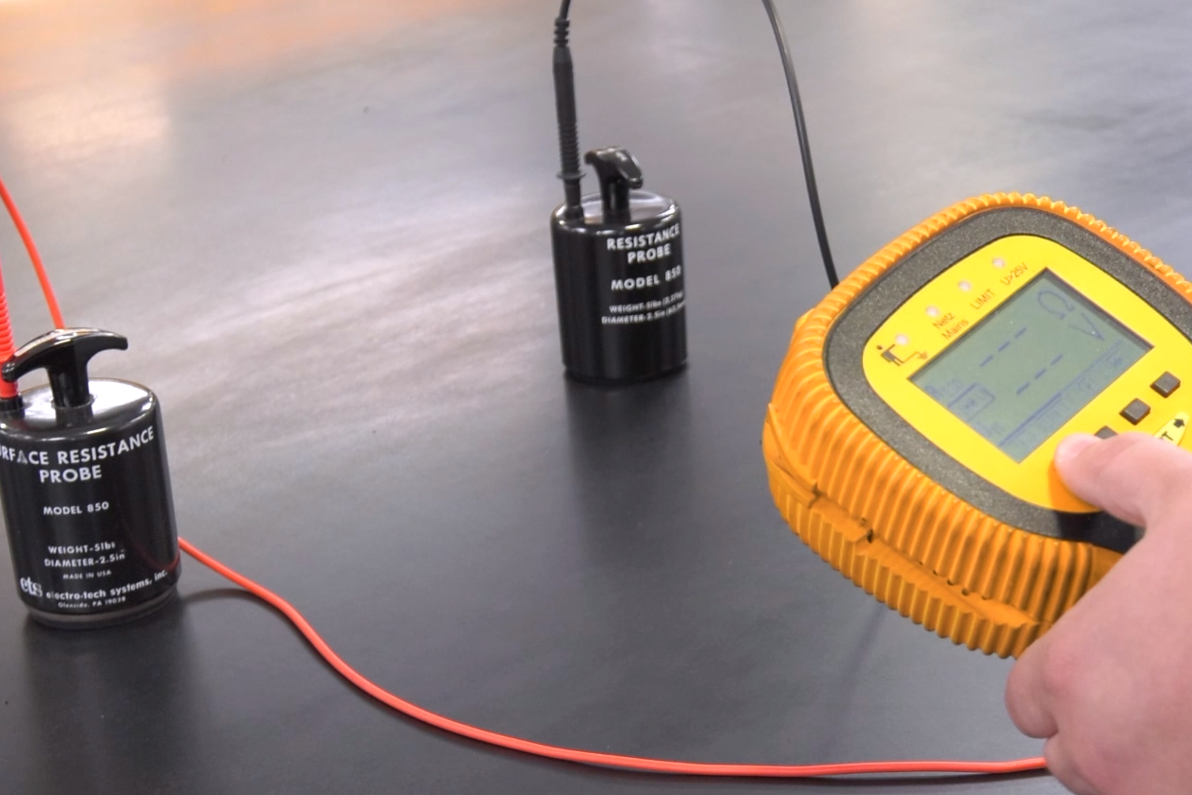
In order to prevent electrostatic discharges, there are some effective countermeasures that prevent sudden discharges from causing costly consequences to electronic components and assemblies or dust explosions. Murdotec’s dissipative plastics help to safely equip working environments by avoiding or minimizing charges by dissipating or enabling uniform discharge.
Tensile testing:
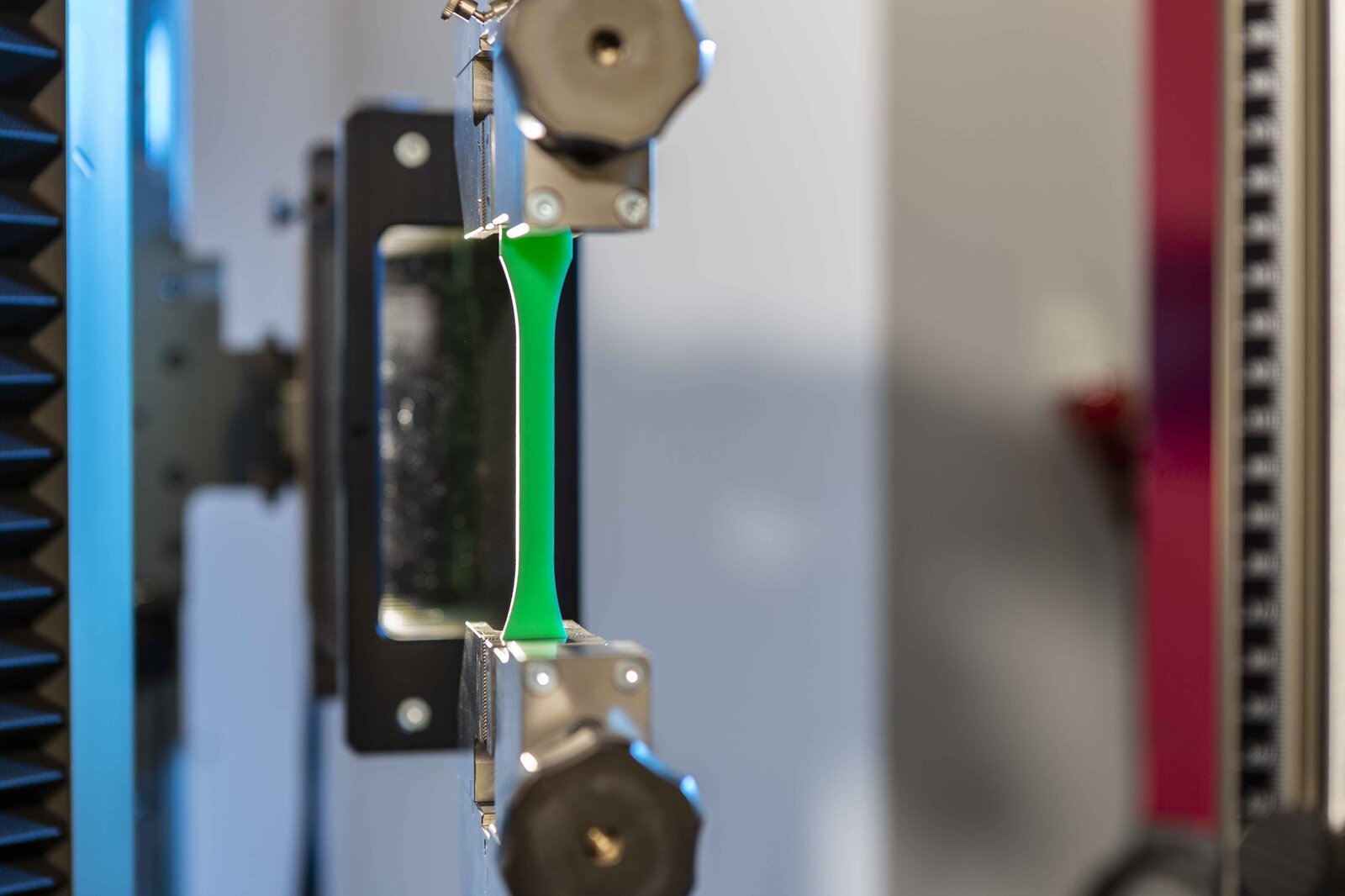
Tensile testing is an essential method for determining the mechanical properties of plastics. It provides important information about the behavior of a material under tensile load, including tensile strength, elongation, and modulus. These properties are critical to the selection and application of plastics in various technical and industrial fields. Our laboratory can perform tensile tests on our resins at temperatures ranging from 23°C to 250°C.
Metal detection:
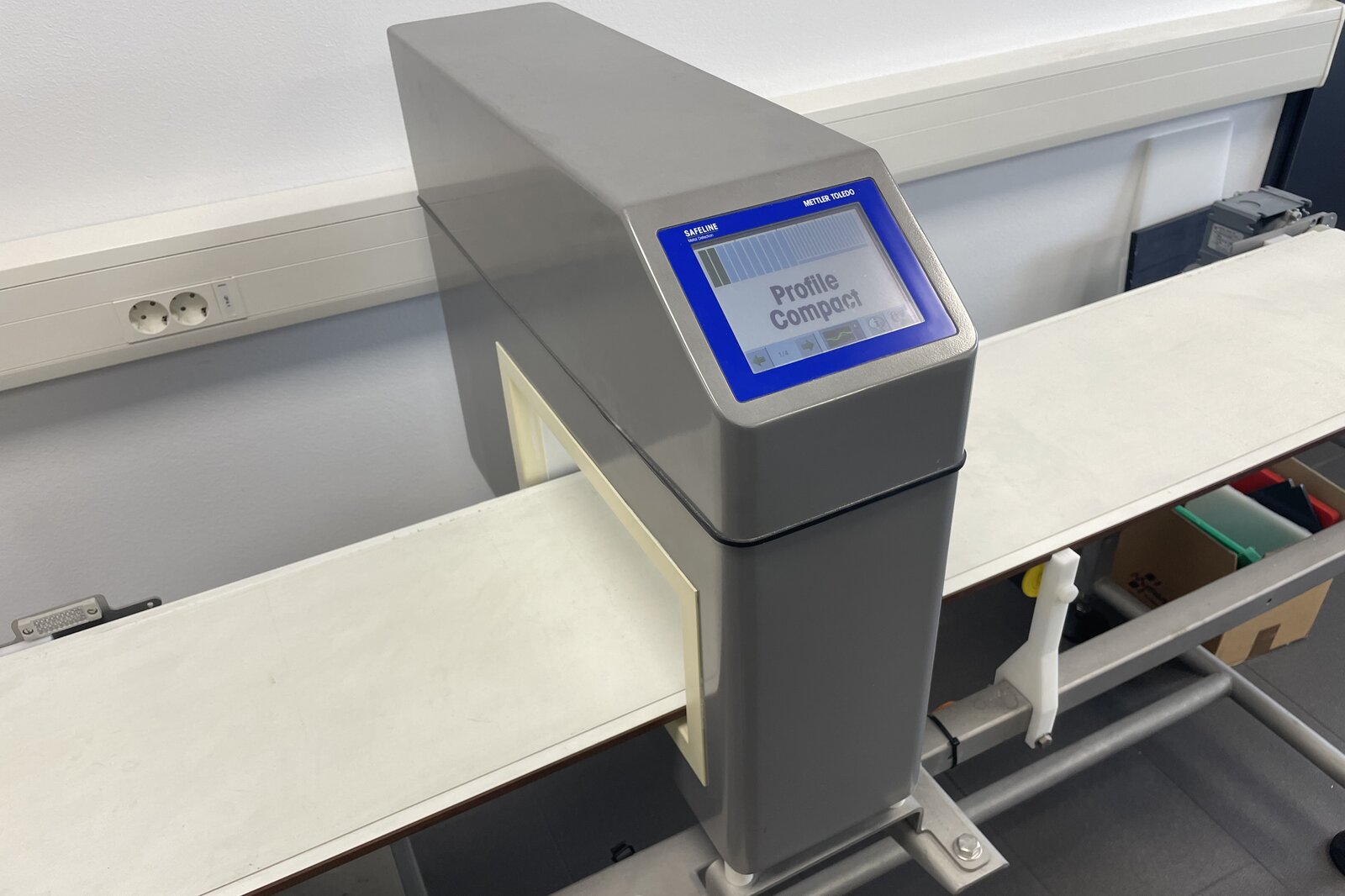

Metal detection is used to check the detectability of material residues. This property is essential in the food industry in particular.
Thin-section microscopy:
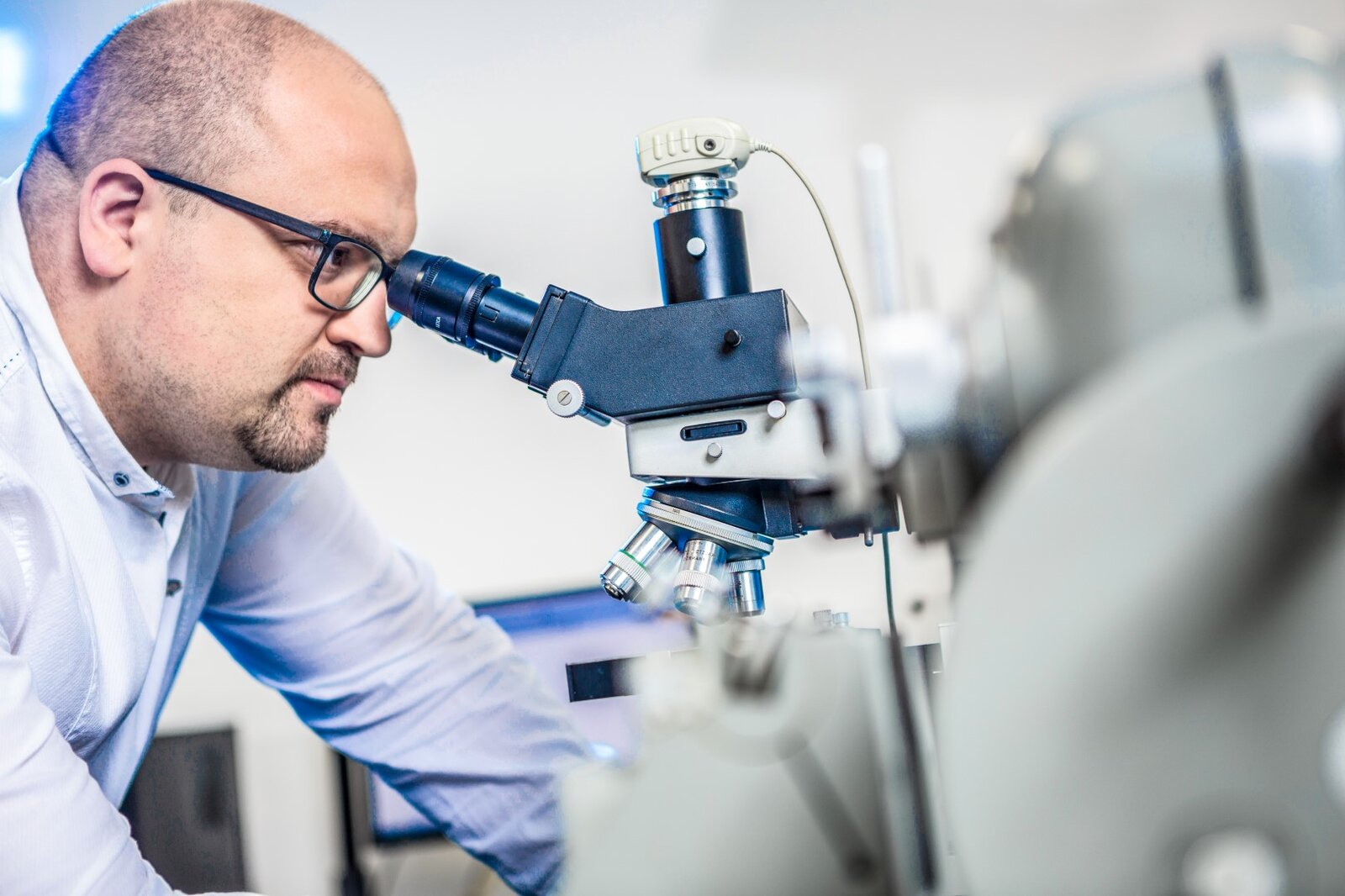

Microscopic examinations of plastics can be used to evaluate plastic molded parts with regard to processing and stress. Microscopy enables essential conclusions regarding the elimination of quality problems and their causes.
Infrared spectroscopy
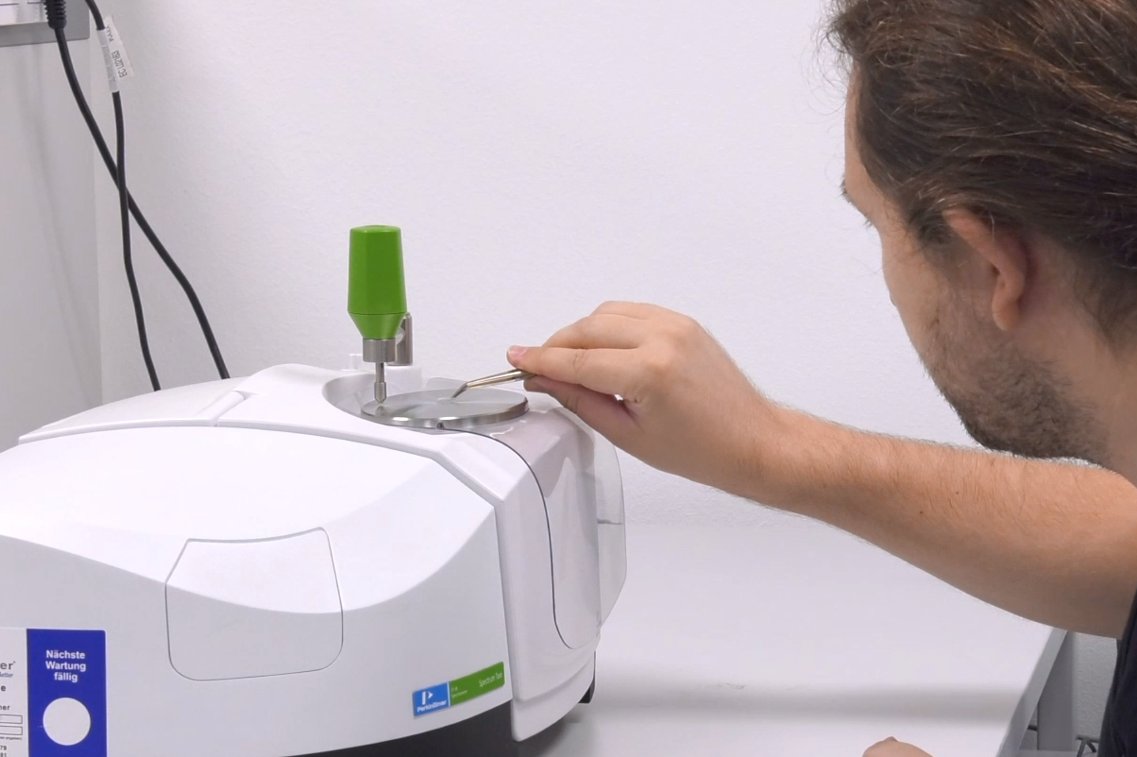

Infrared spectroscopy is a physical test method that works with molecular vibrations using a Fourier transform infrared spectrometer. This method can be used to identify substances and determine material properties. The molecules are irradiated with an infrared laser and the range in which the bonds of the molecules vibrate, absorbing part of the energy, is measured. The transmission, i.e. the unabsorbed energy of the laser, is determined accordingly and displayed in the form of a spectrum. The resulting spectrum is molecule-specific, so each substance has an individual band pattern. These spectra are compared with one another in order to identify materials based on references via a matching system.
Load Change Test Bench:
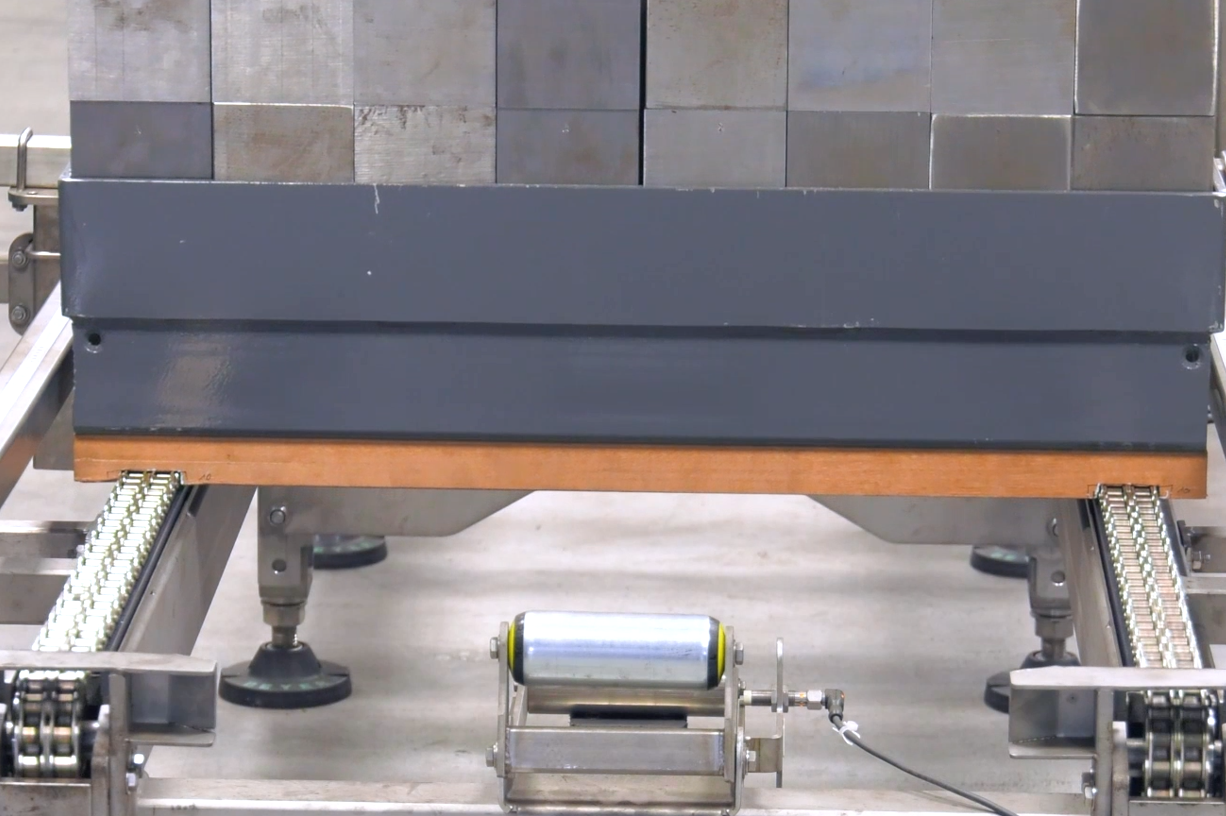
As a practice-oriented long-term test, the load change test bench is an in-house development derived from our material development and testing. It is used to test slide rails made from various different materials. The focus of the test bench is on the durability and durability of the materials, whereby the specific wear profiles that occur in long-term tests are also considered. The load change test bench simulates real conveyor operation. A pallet with additional weight moves back and forth on the sliding rails, each made of different plastics from the Murtfeldt Group, for about 170 days.
Laboratory press:
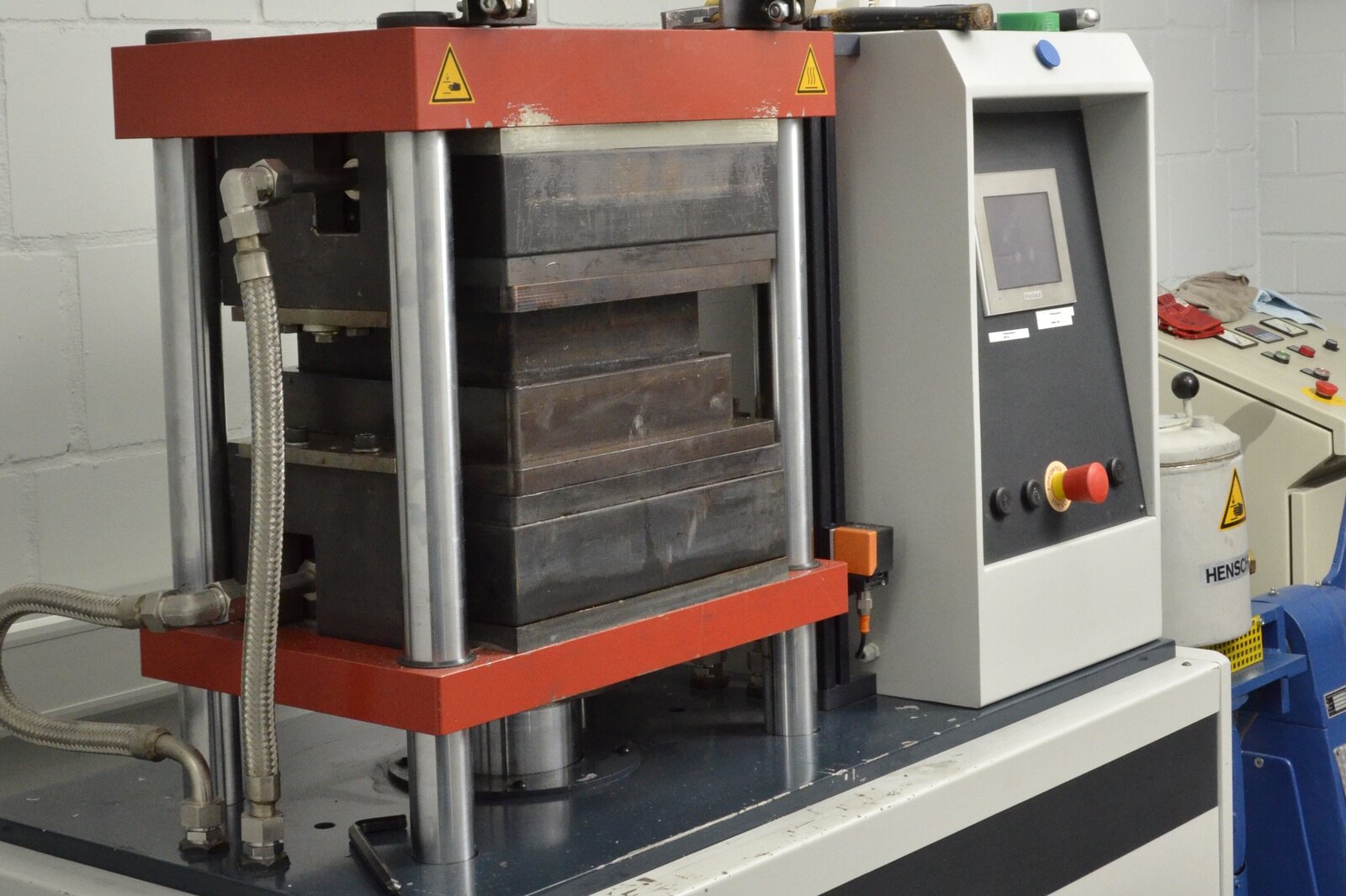

A laboratory press is a device used in scientific and industrial laboratories to perform a variety of pressing operations. It plays an important role in materials research, sample preparation, and quality control.
Ultrasonic measurement:
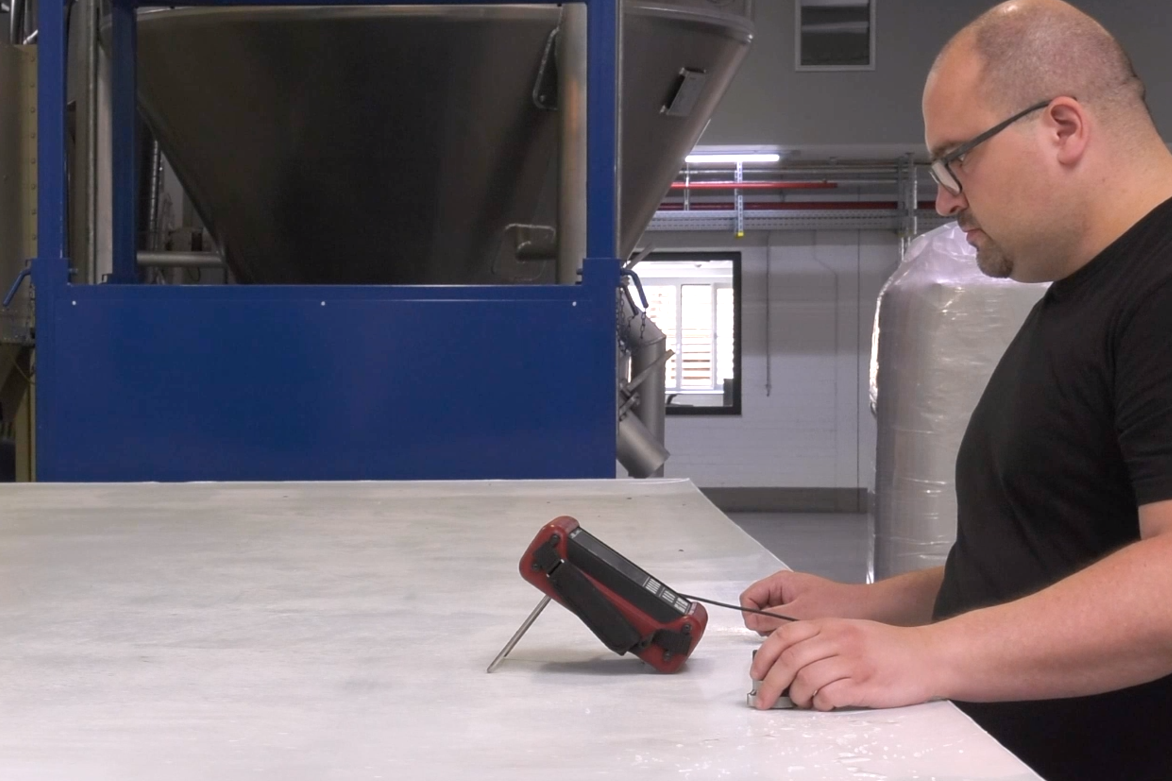

Ultrasonic measurement is a common method for testing plastics and other materials. It is used to determine material thickness and to detect defects. The technique is based on the propagation of high frequency sound waves through the material. It detects cracks, inclusions, delaminations, or other discontinuities in the material. This method is non-destructive and can be used during production.
MVR/MFR:

Melt Mass Flow Rate (MFR) and Melt Volume Flow Rate (MVR) are used to characterize the flow behavior of thermoplastics. Both constitute a single value indirectly proportional to the viscosity at a relatively low shear rate.
